RISCV官网的manual是下面两个
The specifications shown below represent the current, ratified and published releases.
- Volume 1, Unprivileged Specification version 20191213 [PDF]
- Volume 2, Privileged Specification version 20211203 [PDF]
我发现github上有最新的,因此选择最新的manual查看
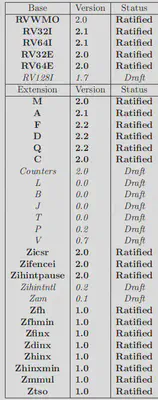
三种状态
- Ratified(批准的)
- Frozen(are not expected to change significantly before being put up for ratification)
- Draft(are expected to change before ratification)
Terminology
- platform:可以包含一个或多个RISC-V兼容的核心以及RISC-V不兼容的核心、固定功能的加速器、多种物理内存架构、IO设备以及interconnect来讲这些组件相连。
- core:一个包含独立取指单元的component。一个核心可能通过超线程技术支持多个hardware threads(harts)。
- coprocessor:一个附属在RISC-V core的单元,is mostly sequenced by a RISC-V instruction stream, 通常也包含额外的架构状态和指令集扩展(extension)
- accelerator:表示非可编程的特定功能的单元或者一个可以自动针对特定任务的core
Software Execution Environments and Harts
Execution Environments Interface(EEI)定义了程序的初始转台、harts的类型以及数量、内存和IO区域的可访问性和属性,所有合法指令的执行表现。(ISA是EEI的一个组件)EEI的例子包括Linux application binary interface(ABI)、RISC-V supervisor binary interface(SBI),EEI的实现可以是纯软件、纯硬件或者软硬结合。实现例子包括:
- Bare metal
- OS
- hypervisor
- emulators, such as Spike, QEMU or rv8, which emulate RISC-V harts on an underlying x86 system
从运行在execution environment的软件角度来看,hart是可以自动取指执行的资源。(抽象的执行资源,而不是软件层面上的线程)
ISA Overview
A RISC-V ISA is defined as a base integer ISA, which must be present in any implementation, plus optional extensions to the base ISA.
这个base integer ISA和早期的RISC处理器指令非常相似,除了没有branch delay slot,以及拥有对可选变长指令编码的支持。
RISC-V实际上是相关ISA的家族,目前包含四个基础的ISA,每一个都有不同宽度和数量的整数寄存器和对应的地址空间。主要的base integer variants有RV32I和RV64I。提供了32bit和64bit的地址空间。我们使用XLEN来表示证书寄存器的位数。在RISC-V中,补码用来表示有符号整数。
The four base ISAs in RISC-V are treated as distinct base ISAs. A common question is why is there not a single ISA, and in particular, why is RV32I not a strict subset of RV64I? Some earlier ISA designs (SPARC, MIPS) adopted a strict superset policy when increasing address space size to support running existing 32-bit binaries on new 64-bit hardware.
RISC-V支持自制扩展,可以扩展一个或者多个可选的指令集,每一个指令集编码空间被划分为三个不重叠的三类:
- standard
- reserved:saved for future
- custom:available for vendor-specific non-standard extensions
为了支持更通用的软件发展,一系列标准extensions被定义
- I(Integer)
- M(Multiply)
- A(Atomic)
- F(Floating-point)
- D(Double-precision floating-point)
- C(Compressed):提供了16bits形式的指令
Memory
RISC-V地址空间为2XLEN bytes。
- word:32 bits(4 bytes)
- halfword:16 bits(2 bytes)
- doubleword:64 bits(8 bytes)
- quadword:128 bits(16 bytes)
The memory address space is circular, so that the byte at address 2XLEN −1 is adjacent to the byte at address zero. Accordingly, memory address computations done by the hardware ignore overflow and instead wrap around modulo 2XLEN.
execution environment定义了硬件资源到hart地址空间的映射。
执行RISC-V机器指令包含一个或多个memory access,被划分为implicit和explict访问两种。当执行指令时,一个implicit memory read发生来获取编码的指令。load和store指令会执行explicit memory read or write。
RISC-V默认的内存一致性模型是Weak Memory Ordering(RVWMO),定义在17章。可选的是,具体的实现可以才哟个更强的模型,比如Total Store Ordering,定义在26章。由于RVWMO是最弱的模型,因此RISCV的实现和其他模型都可以兼容。针对隐式的内存读写,软件必须执行fence或者cache-control指令来确保内存访问的特定读写。
Exceptions Traps and Interrupts
- exception: unusual condition occurring at run time associated with an instruction in the current RISC-V hart
- interrupt: an external asynchronous event that may cause a RISC-V hart to experience an unexpected transfer of control.
- trap to refer to the transfer of control to a trap handler caused by either an exception or an interrupt
从运行在execution environment的软件角度来看,harts遇到的traps可以有如下四种效果:
- contained trap:对软件来说是可见的。
- requested trap:请求environment代表软件做某些事情,如system call。在这种情况,有可能不会返回到harts中执行,比如system call导致environment终结或者删除该harts。
- invisible trap:EE handle完之后转移会harts执行,软件并不知情。例子有emulate missing instructions,在demand-paged环境中处理缺页。
- fatal trap:代表fatal failure,导致EE终止。例子包括虚拟内存页保护机制出现问题。每一个EEI需要定义execution如何终止且被报告给外部环境。
](/post/riscv_chapter1/featured_hud5be8e3b21de53bd9378a1834e4ad2bc_2568_1800x310_fit_q75_h2_lanczos_3.webp)